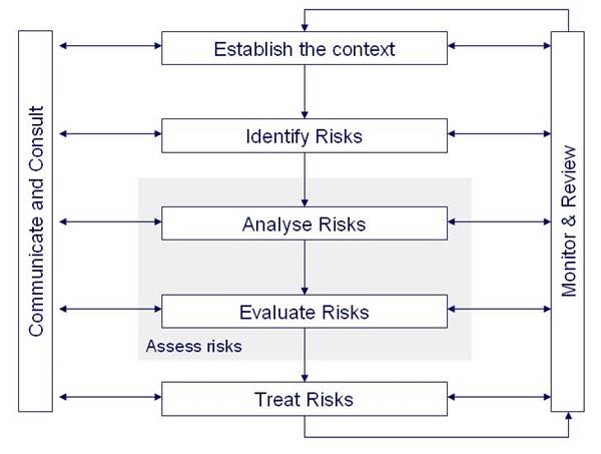
Fatigue Hazard Analysis Risk Assessments
Fatigue Hazard Analysis (FHA) risk assessments can play a significant role in an organisation’s journey towards a comprehensive Fatigue Risk Management System. It is at the heart of our Risk-Based Approach to fatigue management.
Fatigue Hazard Analysis risk assessments are designed to establish a bridge between the Fatigue Risk Management System (FRMS) at an organisational level, and the procedures, activities and treatments required at an operational level.
The workshops draw on the knowledge of experienced staff to discuss fatigue related incidents that could, or have already occurred in the line of their day-to-day duties.
This interactive process is a recognised way to develop the appropriate controls and protection for tasks exposed or vulnerable to fatigue.
Each workshop is focused on a single task group of employees, such as pilots or nurses, and typically runs for between 1.5 – 2 days. All participants are encouraged to speak about their practical experiences of fatigue related risks, in order to achieve the following objectives:
- Identify key operational tasks or day-to-day activities considered to present the greatest fatigue-related risks.
- Create a Hazard Catalogue and assign risk likelihood and consequence ratings for the task hazards.
- Derive a risk tolerance boundary based on the group’s collective view of the acceptability of varying levels of likelihood and consequence.
- Develop risk improvement actions for the highest-risk hazards, and as a priority for hazards outside of the participants’ risk tolerance boundary.
- Determine an hours of work Fatigue Tolerance Level (FTL) for the role, taking into account the fatigue-related risks assessed and other relevant information presented at the workshop.
- Assist or support management in reducing fatigue-related risks.